- Introduction
- 1. 开始
- 2. 核心功能
- 3. NETTY BY EXAMPLE
- 4. 高级主题
- Published with GitBook
添加 WebSocket 支持
WebSocket 通过“Upgrade handshake(升级握手)”从标准的 HTTP 或HTTPS 协议转为 WebSocket。因此,使用 WebSocket 的应用程序将始终以 HTTP/S 开始,然后进行升级。在什么时候发生这种情况取决于具体的应用;它可以是在启动时,或当一个特定的 URL 被请求时。
在我们的应用中,当 URL 请求以“/ws”结束时,我们才升级协议为WebSocket。否则,服务器将使用基本的 HTTP/S。一旦升级连接将使用的WebSocket 传输的所有数据。
下面看下服务器的逻辑
Figure 11.2 Server logic

#1客户端/用户连接到服务器并加入聊天
#2 HTTP 请求页面或 WebSocket 升级握手
#3服务器处理所有客户端/用户
#4响应 URI “/”的请求,转到 index.html
#5如果访问的是 URI“/ws” ,处理 WebSocket 升级握手
#6升级握手完成后 ,通过 WebSocket 发送聊天消息
处理 HTTP 请求
本节实现处理 HTTP 请求,生成页面用来访问“聊天室”,并且显示发送的消息。
下面代码 HttpRequestHandler,是一个用来处理 FullHttpRequest 消息的 ChannelInboundHandler 的实现。注意,忽略 "/ws" URI 的请求。
Listing 11.1 HTTPRequestHandler
public class HttpRequestHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<FullHttpRequest> { //1
private final String wsUri;
private static final File INDEX;
static {
URL location = HttpRequestHandler.class.getProtectionDomain().getCodeSource().getLocation();
try {
String path = location.toURI() + "index.html";
path = !path.contains("file:") ? path : path.substring(5);
INDEX = new File(path);
} catch (URISyntaxException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to locate index.html", e);
}
}
public HttpRequestHandler(String wsUri) {
this.wsUri = wsUri;
}
@Override
public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest request) throws Exception {
if (wsUri.equalsIgnoreCase(request.getUri())) {
ctx.fireChannelRead(request.retain()); //2
} else {
if (HttpHeaders.is100ContinueExpected(request)) {
send100Continue(ctx); //3
}
RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile(INDEX, "r");//4
HttpResponse response = new DefaultHttpResponse(request.getProtocolVersion(), HttpResponseStatus.OK);
response.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/html; charset=UTF-8");
boolean keepAlive = HttpHeaders.isKeepAlive(request);
if (keepAlive) { //5
response.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_LENGTH, file.length());
response.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONNECTION, HttpHeaders.Values.KEEP_ALIVE);
}
ctx.write(response); //6
if (ctx.pipeline().get(SslHandler.class) == null) { //7
ctx.write(new DefaultFileRegion(file.getChannel(), 0, file.length()));
} else {
ctx.write(new ChunkedNioFile(file.getChannel()));
}
ChannelFuture future = ctx.writeAndFlush(LastHttpContent.EMPTY_LAST_CONTENT); //8
if (!keepAlive) {
future.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); //9
}
}
}
private static void send100Continue(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.CONTINUE);
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
1.扩展 SimpleChannelInboundHandler 用于处理 FullHttpRequest信息
2.如果请求是 WebSocket 升级,递增引用计数器(保留)并且将它传递给在 ChannelPipeline 中的下个 ChannelInboundHandler
3.处理符合 HTTP 1.1的 "100 Continue" 请求
4.读取 index.html
5.判断 keepalive 是否在请求头里面
6.写 HttpResponse 到客户端
7.写 index.html 到客户端,判断 SslHandler 是否在 ChannelPipeline 来决定是使用 DefaultFileRegion 还是 ChunkedNioFile
8.写并刷新 LastHttpContent 到客户端,标记响应完成
9.如果 keepalive 没有要求,当写完成时,关闭 Channel
HttpRequestHandler 做了下面几件事,
- 如果该 HTTP 请求被发送到URI “/ws”,调用 FullHttpRequest 上的 retain(),并通过调用 fireChannelRead(msg) 转发到下一个 ChannelInboundHandler。retain() 是必要的,因为 channelRead() 完成后,它会调用 FullHttpRequest 上的 release() 来释放其资源。 (请参考我们先前的 SimpleChannelInboundHandler 在第6章中讨论)
- 如果客户端发送的 HTTP 1.1 头是“Expect: 100-continue” ,将发送“100 Continue”的响应。
- 在 头被设置后,写一个 HttpResponse 返回给客户端。注意,这是不是 FullHttpResponse,唯一的反应的第一部分。此外,我们不使用 writeAndFlush() 在这里 - 这个是在最后完成。
- 如果没有加密也不压缩,要达到最大的效率可以是通过存储 index.html 的内容在一个 DefaultFileRegion 实现。这将利用零拷贝来执行传输。出于这个原因,我们检查,看看是否有一个 SslHandler 在 ChannelPipeline 中。另外,我们使用 ChunkedNioFile。
- 写 LastHttpContent 来标记响应的结束,并终止它
- 如果不要求 keepalive ,添加 ChannelFutureListener 到 ChannelFuture 对象的最后写入,并关闭连接。注意,这里我们调用 writeAndFlush() 来刷新所有以前写的信息。
这里展示了应用程序的第一部分,用来处理纯的 HTTP 请求和响应。接下来我们将处理 WebSocket 的 frame(帧),用来发送聊天消息。
WebSocket frame
WebSockets 在“帧”里面来发送数据,其中每一个都代表了一个消息的一部分。一个完整的消息可以利用了多个帧。
处理 WebSocket frame
WebSocket "Request for Comments" (RFC) 定义了六中不同的 frame; Netty 给他们每个都提供了一个 POJO 实现 ,见下表:
Table 11.1 WebSocketFrame types
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| BinaryWebSocketFrame | contains binary data |
| TextWebSocketFrame | contains text data |
| ContinuationWebSocketFrame | contains text or binary data that belongs to a previous BinaryWebSocketFrame or TextWebSocketFrame |
| CloseWebSocketFrame | represents a CLOSE request and contains close status code and a phrase |
| PingWebSocketFrame | requests the transmission of a PongWebSocketFrame |
| PongWebSocketFrame | sent as a response to a PingWebSocketFrame |
我们的程序只需要使用下面4个帧类型:
- CloseWebSocketFrame
- PingWebSocketFrame
- PongWebSocketFrame
- TextWebSocketFrame
在这里我们只需要显示处理 TextWebSocketFrame,其他的会由 WebSocketServerProtocolHandler 自动处理。
下面代码展示了 ChannelInboundHandler 处理 TextWebSocketFrame,同时也将跟踪在 ChannelGroup 中所有活动的 WebSocket 连接
Listing 11.2 Handles Text frames
public class TextWebSocketFrameHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<TextWebSocketFrame> { //1
private final ChannelGroup group;
public TextWebSocketFrameHandler(ChannelGroup group) {
this.group = group;
}
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception { //2
if (evt == WebSocketServerProtocolHandler.ServerHandshakeStateEvent.HANDSHAKE_COMPLETE) {
ctx.pipeline().remove(HttpRequestHandler.class); //3
group.writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame("Client " + ctx.channel() + " joined"));//4
group.add(ctx.channel()); //5
} else {
super.userEventTriggered(ctx, evt);
}
}
@Override
public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, TextWebSocketFrame msg) throws Exception {
group.writeAndFlush(msg.retain()); //6
}
}
1.扩展 SimpleChannelInboundHandler 用于处理 TextWebSocketFrame 信息
2.覆盖userEventTriggered() 方法来处理自定义事件
3.如果接收的事件表明握手成功,从 ChannelPipeline 删除HttpRequestHandler ,这样就不会有进一步的 HTTP 消息被接收
4.写一条消息给所有的已连接 WebSocket 客户端,通知一个新的 Channel 连接上来了
5.添加新的 WebSocket Channel 到 ChannelGroup 中,这样它就能收到所有的信息
6.保留收到的消息,并通过 writeAndFlush() 给所有连接的客户端。
上面显示了 TextWebSocketFrameHandler 仅作了几件事:
- 当WebSocket 与新客户端已成功握手完成,通过写入信息到 ChannelGroup 中的 Channel 来通知所有连接的客户端,然后添加新 Channel 到 ChannelGroup
- 如果接收到 TextWebSocketFrame,调用 retain() ,并将其写、刷新到 ChannelGroup,使所有连接的 WebSocket Channel 都能接收到它。和以前一样,retain() 是必需的,因为当 channelRead0()返回时,TextWebSocketFrame 的引用计数将递减。由于所有操作都是异步的,writeAndFlush() 可能会在以后完成,我们不希望它来访问无效的引用。
由于 Netty 处理了其余大部分功能,唯一剩下的我们现在要做的是初始化 ChannelPipeline 给每一个创建的新的 Channel 。做到这一点,我们需要一个ChannelInitializer
初始化 ChannelPipeline
接下来,我们需要安装我们两个 ChannelHandler 到 ChannelPipeline。为此,我们需要 ChannelInitializer 和实现 initChannel()。看下面 ChatServerInitializer 的代码实现
Listing 11.3 Init the ChannelPipeline
public class ChatServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { //1
private final ChannelGroup group;
public ChatServerInitializer(ChannelGroup group) {
this.group = group;
}
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { //2
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(64 * 1024));
pipeline.addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler());
pipeline.addLast(new HttpRequestHandler("/ws"));
pipeline.addLast(new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/ws"));
pipeline.addLast(new TextWebSocketFrameHandler(group));
}
}
1.扩展 ChannelInitializer
2.添加 ChannelHandler 到 ChannelPipeline
initChannel() 方法设置 ChannelPipeline 中所有新注册的 Channel,安装所有需要的 ChannelHandler。总结如下:
Table 11.2 ChannelHandlers for the WebSockets Chat server
| ChannelHandler | 职责 |
|---|---|
| HttpServerCodec | Decode bytes to HttpRequest, HttpContent, LastHttpContent.Encode HttpRequest, HttpContent, LastHttpContent to bytes. |
| ChunkedWriteHandler | Write the contents of a file. |
| HttpObjectAggregator | This ChannelHandler aggregates an HttpMessage and its following HttpContents into a single FullHttpRequest or FullHttpResponse (depending on whether it is being used to handle requests or responses).With this installed the next ChannelHandler in the pipeline will receive only full HTTP requests. |
| HttpRequestHandler | Handle FullHttpRequests (those not sent to "/ws" URI). |
| WebSocketServerProtocolHandler | As required by the WebSockets specification, handle the WebSocket Upgrade handshake, PingWebSocketFrames,PongWebSocketFrames and CloseWebSocketFrames. |
| TextWebSocketFrameHandler | Handles TextWebSocketFrames and handshake completion events |
该 WebSocketServerProtocolHandler 处理所有规定的 WebSocket 帧类型和升级握手本身。如果握手成功所需 ChannelHandler 被添加到管道和那些不再需要则被去除。管道升级之前的状态如下图。这代表了 ChannelPipeline 刚刚经过 ChatServerInitializer 初始化。
Figure 11.3 ChannelPipeline before WebSockets Upgrade
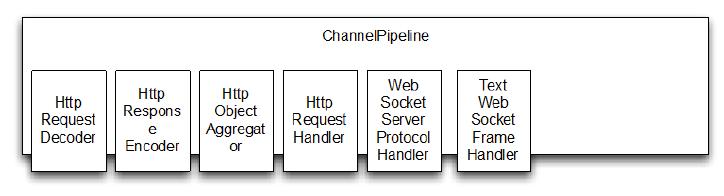
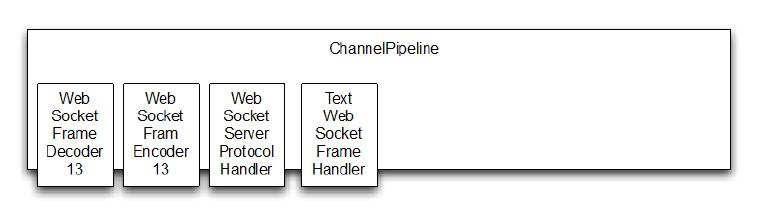
握手升级成功后 WebSocketServerProtocolHandler 替换HttpRequestDecoder 为 WebSocketFrameDecoder,HttpResponseEncoder 为WebSocketFrameEncoder。 为了最大化性能,WebSocket 连接不需要的 ChannelHandler 将会被移除。其中就包括了 HttpObjectAggregator 和 HttpRequestHandler
下图,展示了 ChannelPipeline 经过这个操作完成后的情况。注意 Netty 目前支持四个版本 WebSocket 协议,每个通过其自身的方式实现类。选择正确的版本WebSocketFrameDecoder 和 WebSocketFrameEncoder 是自动进行的,这取决于在客户端(在这里指浏览器)的支持(在这个例子中,我们假设使用版本是 13 的 WebSocket 协议,从而图中显示的是 WebSocketFrameDecoder13 和 WebSocketFrameEncoder13)。
Figure 11.4 ChannelPipeline after WebSockets Upgrade
引导
最后一步是 引导服务器,设置 ChannelInitializer
public class ChatServer {
private final ChannelGroup channelGroup = new DefaultChannelGroup(ImmediateEventExecutor.INSTANCE);//1
private final EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
private Channel channel;
public ChannelFuture start(InetSocketAddress address) {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); //2
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(createInitializer(channelGroup));
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(address);
future.syncUninterruptibly();
channel = future.channel();
return future;
}
protected ChannelInitializer<Channel> createInitializer(ChannelGroup group) { //3
return new ChatServerInitializer(group);
}
public void destroy() { //4
if (channel != null) {
channel.close();
}
channelGroup.close();
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
if (args.length != 1) {
System.err.println("Please give port as argument");
System.exit(1);
}
int port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
final ChatServer endpoint = new ChatServer();
ChannelFuture future = endpoint.start(new InetSocketAddress(port));
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
endpoint.destroy();
}
});
future.channel().closeFuture().syncUninterruptibly();
}
}
1.创建 DefaultChannelGroup 用来 保存所有连接的的 WebSocket channel
2.引导 服务器
3.创建 ChannelInitializer
4.处理服务器关闭,包括释放所有资源